Ranking is one more searching engines function that you have to know about.
How answer engines rank URLs
Ranking is a complex process of search engines making sure that users get relevant results for a question entered into the search bar. In other words, it is search results ordering by most relevant to least relevant for a particular query.
Search engines use algorithms, formulas, or processes by which stored information is collected and ordered in meaningful ways to determine the relevance of the results. Nowadays, the quality of search results is high because these algorithms have gone through many changes over the years. A bright example of that improvement is Google. It regularly makes algorithm adjustments. But sometimes these updates are minor quality tweaks. Whereas others show core/broad algorithm updates deployed to tackle a specific issue. For example, tackling link spam – Penguin.
It is a fact that algorithms frequently vary, so what is the reason for those changes?
Although Google doesn’t always disclose specifics of their doing, we do understand that Google aims to improve overall search quality. By asking such question as “why are algorithms updated so often”, Google will answer with something along the lines of: “We’re making quality updates all the time.”
This means that, if your site suffered after algorithm adjustments, you should compare it against Google’s Quality Guidelines or Search Quality Rater Guidelines. Both are useful in terms of what search engines aim for.
What search engines want
The primary function of search engines is to answer user’s questions. But why does it appear that SEO is different now than in years past?
It may be compared with individuals who learn a new language.
At the beginning of studying learners cannot understand the language to the full. Over time, their understanding changes, and they learn semantics — the meaning behind language and the connection between words and word-combinations. Practice plays the most important role during studying. Using new language in practice allows one to understand nuance and reply to unclear or incomplete questions.
When search engines were at the beginning of learning our language, it was clearer how to run the system. Let’s consider keyword stuffing. To rank for a particular keyword, you should use it several times on your page. You can make the keyword bold to boost your ranking for that term.
For example, the phrase “beautiful pictures”.
“Welcome to cite with beautiful pictures! We provide the most beautiful pictures on the internet. Enjoy our beautiful pictures! The most beautiful pictures await. Choose the most beautiful picture and download it because a beautiful picture can make you happy and funnier. Some beautiful pictures will become your favorite ones.”
This tactic causes terrible user experiences and had the opposite effect. Instead of enjoying a beautiful picture, people suffered from the annoying hard-to-read text. Possibly it was influential in the past, but this is never the purpose of search engines.
About links in SEO
Talking about links, it is essential to consider two things. Backlinks or “inbound links” means links from other sites that go to your site, while internal links meaning links of the site that point to your other pages – on the same site.
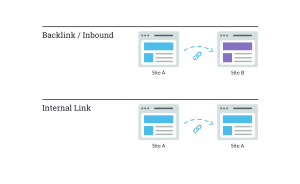
Links are essential components of SEO. Very early on, search engines required assistance in figuring out which URLs were more reliable than others to help them determine how to rank search results. Calculating the number of links that point to any given site helped search engines to do this.
Backlinks work very similarly to real-life WoM (Word-of-Mouth) referrals. Let’s take a hypothetical pizzeria, Tasty pizza, as an example:
-
- Referra :An owner of Tasty Pizza paid to have people who have never visited the pizzeria tell others how good it is.
No referrals = unclear authority
-
- Example: Tasty pizzeria might be good, but you’ve been unable to find anyone who has an opinion so you can’t be sure.
For this purpose PageRank was created. PageRank is a part of Google’s core algorithm and it means a link analysis algorithm named after one of Google’s founders, Larry Page. PageRank aims to estimate the importance of a web page by measuring the quality and quantity of links pointing to it. The more relevant and reliable a web page is, the more links it will have earned. Higher rank within search results depends on natural backlinks from high-authority (trusted) websites.
The role of content in SEO
If links don’t direct searchers to something, they are not useful. That something is content and it is more than just words. It’s anything searchers need — there’s video content, image content, and of course, text. As search engines are answer engines, so content is a way the engines deliver those answers.
When a user performs a search, thousands of possible results appear. But how do search engines select pages and find valuable ones? A place where your page will rank for a given query depends on the quality of content on your page and how well it matches the query’s intent. In other words, does this page match the words that were searched and help fulfill the task the searcher was trying to accomplish?
User satisfaction and task accomplishment are the main points, therefore, no strict benchmarks on how long your content should be, how many times it should contain a keyword, or what you put in your header tags. All those can influence a page’s performance in search, but the focus should be on the users who will be reading the content.
Nowadays there are thousands of ranking signals, but the top three signals include links to your website (which serve as third-party credibility signals), on-page content (quality content that fulfils a searcher’s intent), and RankBrain.
RankBrain: what does it mean?
RankBrain means the machine learning component of Google’s core algorithm. Machine learning is a specific computer program aiming to improve its predictions over time through new observations and training data. In other words, it’s always learning, and because of this, search results should continuously be better.
If RankBrain sees a lower ranking URL providing a better result to users than the higher-ranking URLs, RankBrain will adjust those results. It moves the more relevant result higher and demotes the lesser relevant pages as a byproduct.

Engagement metrics: correlation, causation, or both?
Engagement metrics are most likely part correlation and part causation with Google rankings.
When we discuss engagement metrics, we mean data that represents how searchers interact with your site from search results. This includes things like:
-
- Clicks (visits from search)
- Time on page (amount of time the visitor spent on a page before leaving it)
- Bounce rate (the percentage of all website sessions where users viewed only one page)
- Pogo-sticking (clicking on an organic result and then quickly returning to the SERP to choose another result)
Lots of tests have proved that engagement metrics correlate with a higher ranking. But causation is still being hotly debated.
What is the conclusion, and what does all this mean for SEOs?
Google will continue leveraging RankBrain to promote the most relevant, helpful content So we need to focus on fulfilling searcher intent more than ever before. Show the best possible information and experience for searchers who might visit your page, and you’ve already taken a significant first step to do well in RankBrain.
Use all we have learned from these three articles about search engines and improve your website. Have any questions? Need help or consultation? Contact us directly, and we will give all the answers.