Once you have a website and you take care of its SEO, you should understand how search engines work, how they analyze your content, get pages indexed, ranked, etc. This is the first part of the research and it is about the basics of search engines and their crawling function. In the next articles we will look through other functions, such as indexing and ranking, so don’t miss it and check the articles out.
Search engines also named as answer engines work with the content by searching, understanding, and organizing it. They provide relevant results to the questions internet users ask.
To find your content in search results, you should take care of its visibility for answer engines. It is the most vital thing concerning SEO: you will never appear in the Search Engine Results Page (SERPs) if your site can’t be detected.
How do search engines work?
Having three main purposes search engines can:
1) Crawl – Scouring the Internet for content, browsing the code/content for each URL they find.
2) Index – Storing and organizing the content received after crawling. An indexed page means it’s in the running to be shown as a result of relevant queries.
3) Rank – Providing the parts of content that satisfy a searcher’s queries. It means the results are ordered from most relevant to least relevant.
Search engine crawling: how does it work?
Crawling is a finding method in which robots (known as crawlers or spiders) receive a command from search engines to find the newest content – it can be a webpage, a picture, a video, etc. Links are the ones that unite all the forms of content.
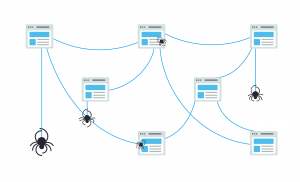
First, Googlebot fetches a few web pages. After that, it follows the links on those pages to get new URLs. Using this way of links, the spider gets fresh content and adds it to the Caffeine index, a huge database that is the storage of discovered URLs, and later this content may be retrieved when a user is searching for information.
Index of Search engine
Search engines are used for processing, storing information found in an index. This massive database accepts all the content from search engines that it is appropriate enough to serve up to searchers.
Search engine ranking
While performing the search, search engines look through their index for relevant content. After that, they select that content to solve the searcher’s request. The ranking is an ordering of search-relevant results. The higher a website is ranked, the more relevant the search engine deems that site is to the query.
Crawling: How do search engines find your pages?
According to the words above, it is vital to ensure that your site gets crawled and indexed. It is a requirement to be discovered in the SERPs. Have a site? First, examine the number of your pages in the index. It will help to recognize whether Google is crawling and finding all the vital pages or not.
If you want to check your indexed pages, use a search operator the «site:yourdomain.com”. Type into the Google search block “site:yourdomain.com” – it will provide results Google has in its index for the site specified. The quantity of results Google shows (see “About XX results” above) isn’t exact. But it shows which webpages are indexed on your site and how they are currently displaying in search results.
There are several reasons for not to be displayed in the search results:
- The site hasn’t been crawled yet because of its novelty.
- The site isn’t linked to any external websites.
- Robots cannot crawl because of your site navigation that stops them.
- The platform has particular code – crawler directives; they block search engines.
- Google has penalized your site for spammy tactics.
How can crawlers find all your actual content?
As you have got acquainted with the tactics for guaranteeing search engine crawlers avoid unimportant content, it is time to find out more about an optimization process that helps Googlebot determine essential webpages.
There are cases when a search engine sees parts of your site by crawling but other sections or pages are obscured. To avoid this, check the answer engines’ ability to find all the content that should be indexed, not just your homepage.
Ask: whether the bot can crawl through your website or not?
Is your content concealed behind login forms?
If your website users have to log in, share their data, or answer surveys to get access to certain content, search engines won’t detect those protected pages. A crawler will not log in.
Can search forms help?
Robots can’t use search forms. Lots of people make a mistake thinking that placing a search box on their site can help and search engines will be able to provide everything their visitors search for.
Is text concealed within non-text content?
You cannot use non-text media forms such as pictures, GIFs, movies, etc. in order to display text that you want to be indexed. Even though search engines can recognize images, it doesn’t mean they can read and understand everything. Make it a rule to add text within the markup of your internet page.
Are search engines following your site navigation?
Crawlers discover your site with the links from other sites; therefore, they need a way of links on your site in order to guide it from one page to another. If you wish a search engine to find a page, but it isn’t linked to any other pages, it’s as good as invisible. Many sites make the crucial mistake by structuring their navigation in ways that are inaccessible to search engines. It hides their ability to get listed in search results.
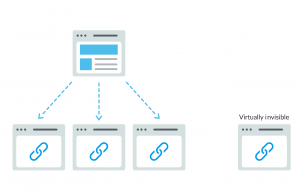
Top-4 navigation mistakes making it impossible for crawlers to see all pieces of your site:
- Mobile navigation that presents different results than your desktop navigation.
- Any navigation where the menu details are not in the HTML, for example, JavaScript-enabled navigations. Google, with its improvements at crawling and understanding Javascript, is still not a perfect process. Put Google in the HTML to ensure something gets found, understood, and indexed.
- Personalization and showing unique navigation to a specific type of visitor VS others, could appear to be cloaking to a search engine crawler.
- Forgetting to link to the main page on your website through your navigation.
Important: links are the pathways crawlers follow to new pages!
It is essential to make sure the website has straightforward navigation and helpful URL folder structures.
The role of sitemaps
A sitemap looks like a list of URLs on your site. It is used by crawlers for discovering and indexing your content. To ensure that Google can find your top priority pages, you need to create a file that meets Google’s requirements. Submit it through Google Search Console.
Submitting a sitemap doesn’t replace the need for good site navigation, it can certainly enable crawlers to follow a path to all of your important webpages.
Have you got clean information architecture?
Information architecture involves the praxis of organizing and labelling content on a site in order to increase efficiency and findability for users. An intuitive information architecture that means saving users from hard thinking about how to flow through your website or to find something, is the best variant of information architecture.
Do crawlers get errors when they try to access your URLs?
There are cases when a spider may encounter errors. It can occur during the process of crawling the URLs on your site. In such case, you may report in the Google Search Console’s “Crawl Errors” to detect URLs on which this might be happening. This report provides information about undiscovered errors and server errors. Server log files can also detect this. Moreover, crawl frequency can also determine errors. But it is a more complex tactic because of its accessing and dissecting server log files. Before you can do anything meaningful with the crawl error report, it’s vital to examine server errors and “not found” errors.
4xx Codes
They are client errors when search engine crawlers can’t access your content due to a wrong syntax or cannot be fulfilled. “404 not found” error is one of the most common 4xx errors. There are several reasons for this error: a URL typo, deleted page, or broken redirect, etc. Getting a 404, means a search engine can’t access the URL. Users hitting a 404 can go out from the site.
5xx Codes
Search engine crawlers can’t access pieces of content due to a server error. 5xx errors are a kind of server errors. They meaning the server the internet page is located on failed to fulfill the searcher or search engine’s request to access the page. The request for the URL timed out usually causes this mistake. In this case Googlebot abandons the claim.
301 redirect
Fortunately, there is a way to notify both searchers and search engines that your page has taken another place. It is a 301 (permanent) redirect. 301 status code means that the page has moved to a new location, so you should avoid redirecting URLs to irrelevant pages URLs where the old URL’s content doesn’t exist. A page might drop in rank position even if it is ranking for a query. It occurs if the content that made a page relevant to that particular query is not there anymore. 301s are a powerful tool, so move URLs responsibly!
302 redirect
You also can use 302 redirecting a page. But this should be reserved for temporary moves and in cases where passing link equity isn’t as big of a concern. 302s could be compared with a road detour. You’re temporarily siphoning traffic through a specific route, but it won’t be like that forever.
Once you have made sure that the site is optimized for crawlability – ensure it can be indexed.



